A Machine Learning Engineer often works with large datasets, trains complex models, and manages extensive computational resources. To navigate these tasks effectively, a solid understanding of Linux commands is helpful. In this article, explore the top 20 Linux commands that every Machine Learning Engineer should know to enhance productivity and streamline their work.
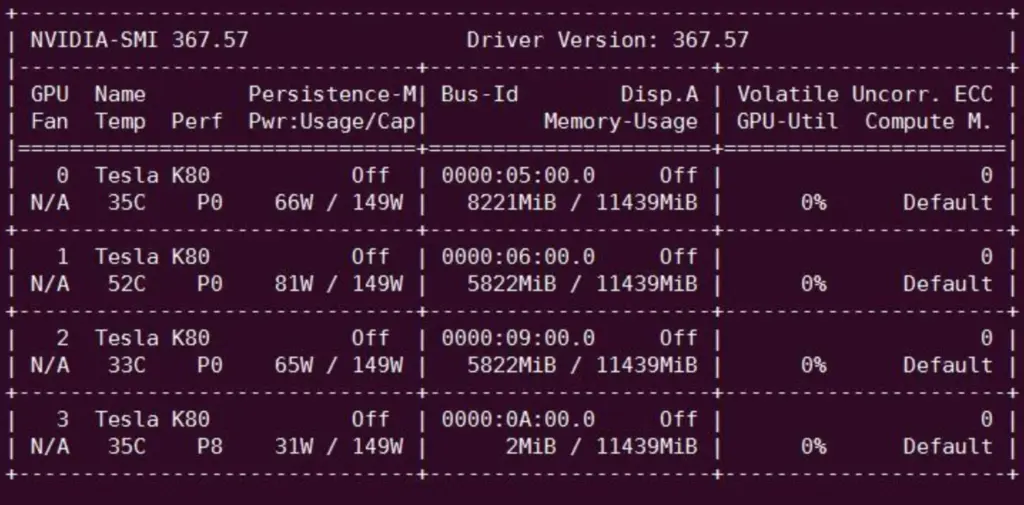
1. nvidia-smi
Get information on the number of GPU devices, memory usage, and utilization.
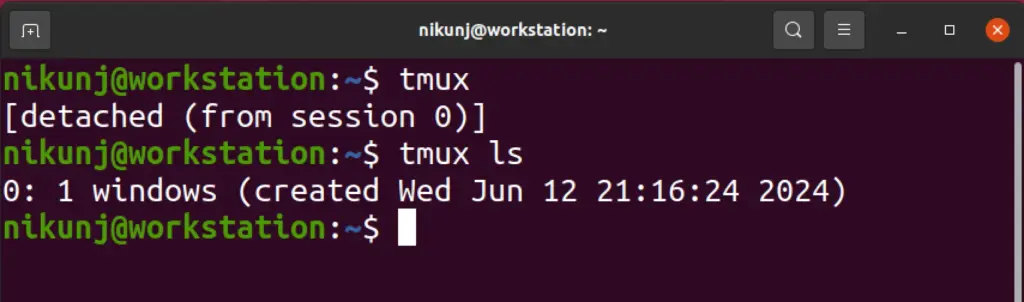
2. tmux
A separate session within a session that keeps running in the background until closed. As model training takes a while, it is essential to execute the ML pipeline inside another session such as tmux.
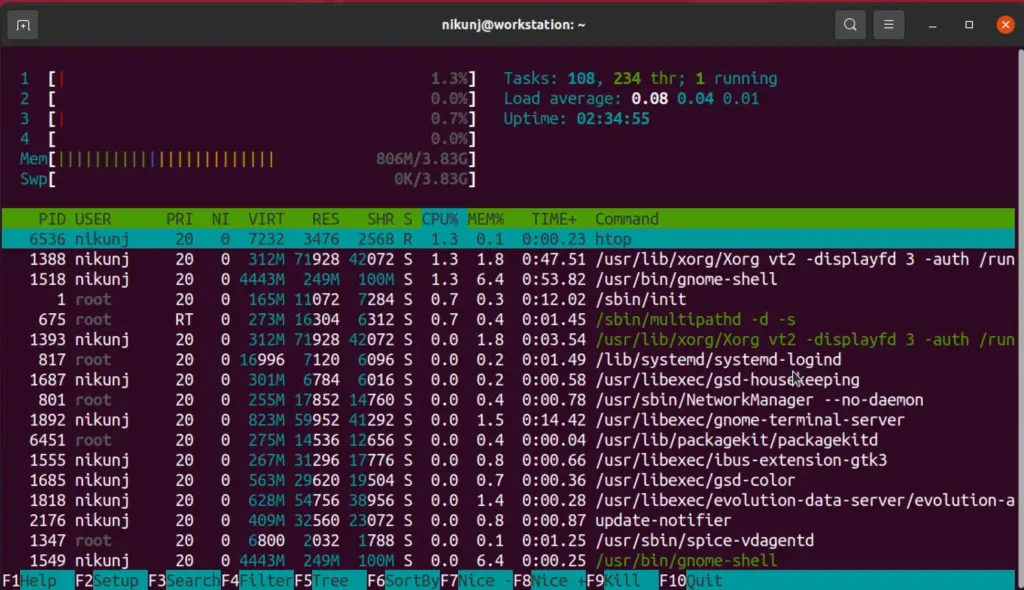
3. htop
View all the processes running on your system using this command. It shows processes from all users. It provides support for the termination of any process.
4. kill [signal] PID
This command can terminate the process using the process id. In Machine Learning there may come a situation where a process is not responding due to an exception or memory resource. In this case, terminating this process is the best choice.
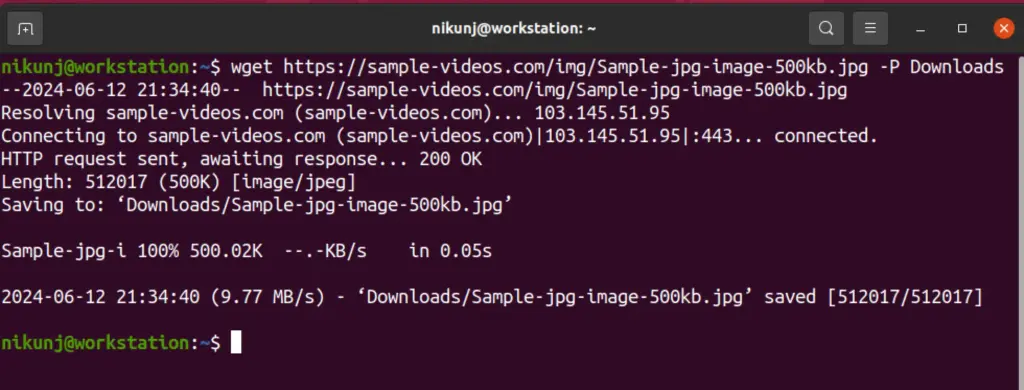
5. wget
As ML engineer this is one of the most commonly used commands to download datasets from the source. Like every command, there are options with the command such as renaming the file name or specifying the directory to save in.
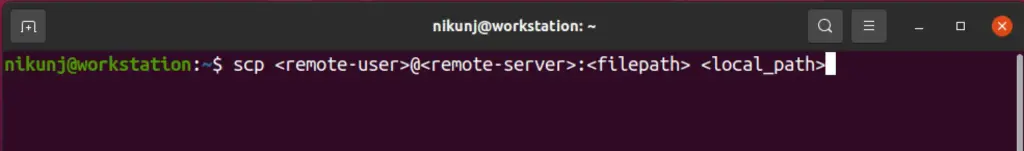
6. scp
Often times may need to transfer files between local and remote servers. This command can assist in transferring files or folders between local and remote servers or even between two remote servers.
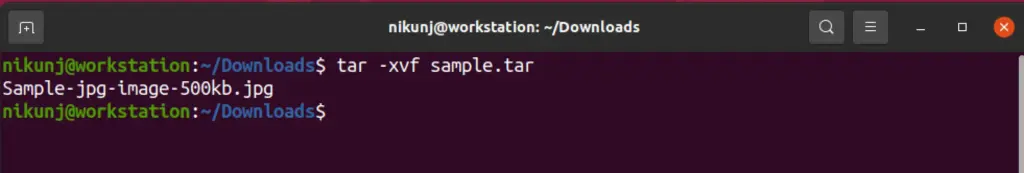
7. tar
As a Machine Learning engineer most of the data is found to be in a tar file. Extracting files and unpacking them can be done with this command.
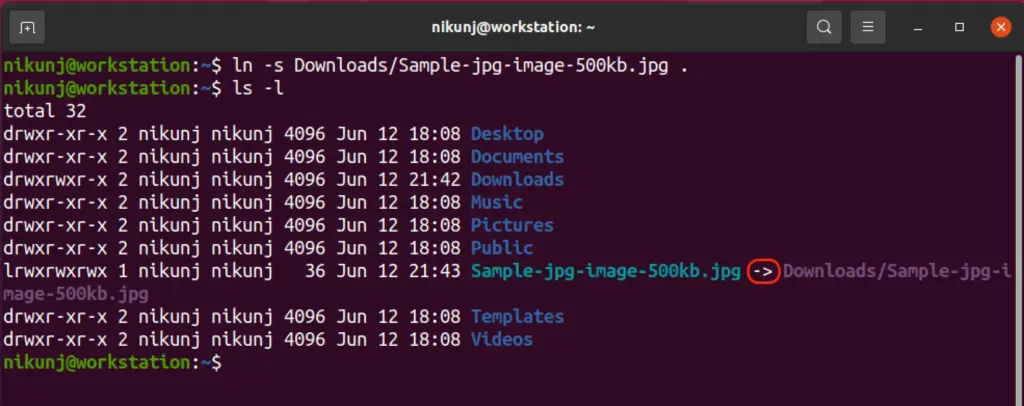
8. ln -s
Databases are huge in size. Often these are stored in some sort of shared SSD or HDD for access. Creating a symbolic link to the database allows creating a shortcut of the files within the home directory that points to the original source.
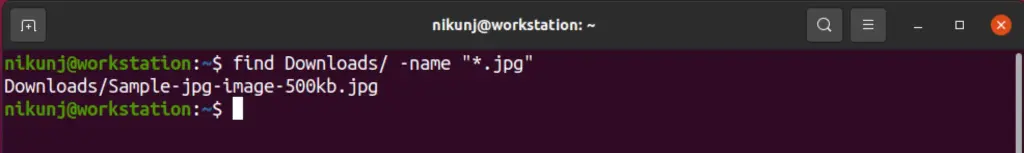
9. find
Often times there may be a need to find a specific file in your database. This command helps to find a specific file or a set of files based on the extension.
10. grep
Finding and displaying certain patterns in a file can be done using this command.
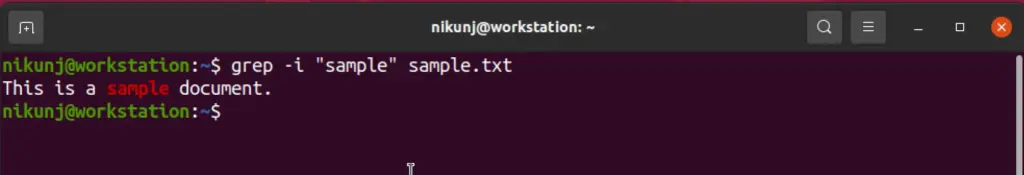
11. head
This command can be used to print the first lines in the files. It is helpful as there may need to verify certain files or take a quick glance at them without opening them.
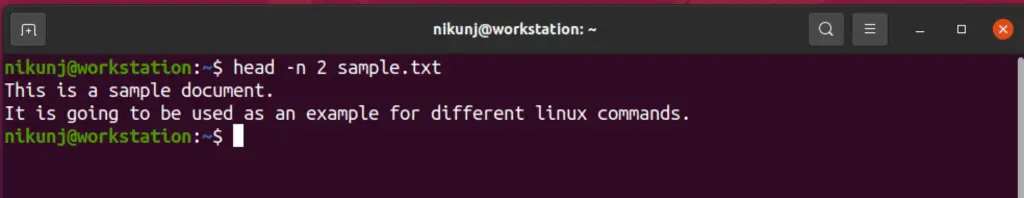
12. chmod
This command helps to change the permission of a file or a folder. As a Machine Learning engineer, there will most commonly require it to create an executable file. Many experts use this more often to prevent access to folders or files such as Database folders or results folders that are shared amongst other collaborators. They may make them as readable files.
13. rm
This removes any file or folder from a certain directory when specified. It is the most common command but if not used correctly then it could turn into a dangerous one.
14. history
During development or debugging, commands or script files need to be re-executed. This command shows every command that has been executed previously.
15. ssh <remote-user>@<remote-ip>
Log in to the server with the username and IP address of the server. Highly recommend to setup the ssh key. There will be no need to enter a password and login will be done securely into your server.
16. vim <filepath>
Terminal editors are extremely helpful in making quick changes in a script or file. vim is one of the popular editors. Other editors such as vi, and nano are also quite popular.
17. bash train.sh
If the script file is not made executable then use bash <script> to execute one. Otherwise, use the chmod command to make it an executable. In a script file lot of commands can be placed. Even provide parameters to the script that can get forwarded to the respective Python scripts that is being run. For example, provide a parameter such as train or test to make sure the relevant Python script is executed.
18. jupyter notebook –no-browser –port=8889
Jupyter notebooks are most widely used in ML and are popular for quick execution and seeing quick results of the code. The command above can execute a jupyter notebook on the server and mount the relevant files from the point of execution.
19. wc
Since dealing with a lot of data, a quick check after the initial download of data is helpful. This command does word count and can be also used to count the number of files in the folder.
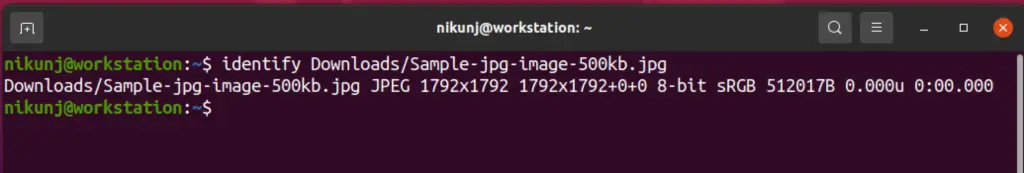
20. identify
Quick info about a particular image such as size or resolution is important in Computer Vision tasks. Install the imagemagick package and use this command to obtain info about a particular image file.